Overview of Policies
Smart Wallets enable seamless crypto experiences with gas sponsorship, batched transactions, and chain abstraction. Secured by non-custodial Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) and enterprise-grade audited smart contract accounts, smart wallets protect user assets with both offchain and onchain safeguards.
Policies allow you to set rules and constraints governing how smart wallets operate, ensuring security and control over onchain actions. Using the policy dashboard, you can easily configure rules such as spending limits, contract allowlists, or denylists. This overview explains how you can leverage policies to further secure your smart wallet.
Key Features:- Granular control: Define allowable actions, such as approved contracts or maximum transfer amounts.
- Scalability: Policies are built on Alchemy’s high-performance RPC and gas sponsorship systems, ensuring seamless operation at scale.
- Composable Security: Policies can be defined onchain or offchain and seamlessly composed to authorize smart wallet operations to multi-layer beyond standard authentication mechanisms.
Offchain Policies (EVM & Solana): Offchain policies shift rule enforcement to Alchemy’s offchain infrastructure. In EVM, these policies can also be composed with the onchain policies to provide multi-layered security.
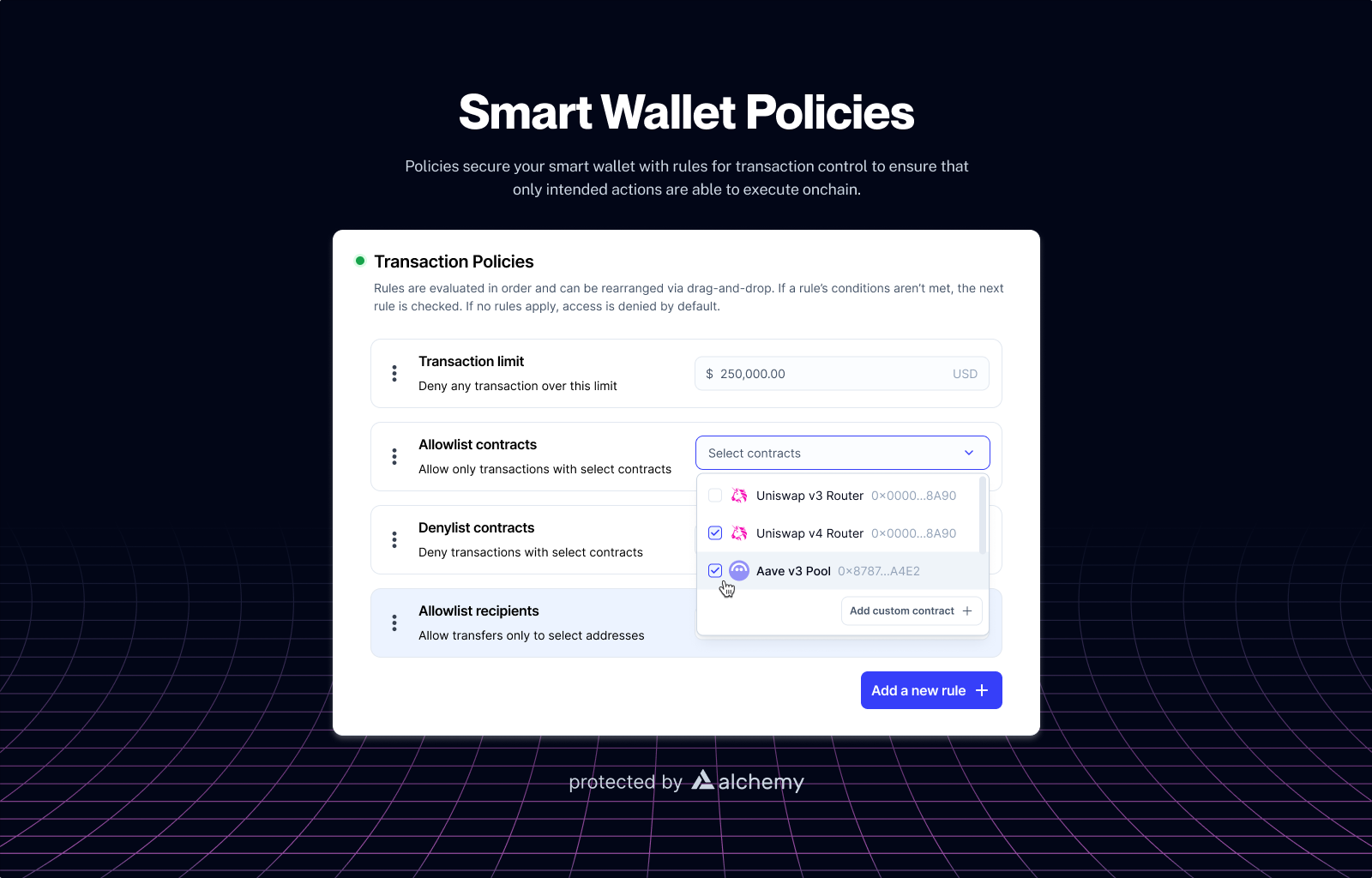
Offchain policies support many rules including:
- Transaction Limits: Restrict the value of transfers (e.g., cap at 1 ETH per transaction or 10 ETH daily) to prevent overspending or unauthorized large moves.
- Contract Allowlists: Limit interactions to approved smart contracts (e.g., Uniswap, Aave), enhancing security by blocking untrusted protocols.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple authentication factors to sign a transaction.
- Chain Restrictions: Limit transactions to only certain chains
- Gas Sponsorship Rules: Define custom conditions for gas sponsorship (e.g. sponsor up to $10 in gas, or first 10 transactions, allowlist/blocklist senders for sponsorship, custom rules, etc.).
Onchain Policies (EVM only): Onchain policies lock in trust, transparency, and developer right to exit — rules baked into smart contracts enforce security and consistency without relying on fragile offchain servers or middlemen. Because the rules are defined onchain, they remain consistent regardless of which key provider is used.
- Transaction Limits: Use onchain modules to restrict the value of transfers (e.g., cap at 1 ETH per transaction or 10 ETH daily) to prevent overspending or unauthorized large moves.
- Contract Allowlists: Use onchain modules to limit interactions to approved smart contracts (e.g., Uniswap, Aave), enhancing security by blocking untrusted protocols.
- Multi-Signature Requirements: Enforce quorum rules (e.g., 2-of-3 signers for high-value transactions), ideal for shared custody, treasury management, or onchain multi-factor authentication.
- Time Restrictions: Allow transactions only within specific time windows (e.g., within the next 24 hours), enabling scheduled operations.
- Gas Sponsorship Rules: Define requirements for paymaster definitions (e.g., require your token is used for gas or that transactions are sponsored under certain conditions).
- Asset-Specific Caps: Use onchain session keys to set limits on ERC-20 token transfers (e.g., max 1000 USDC per action) or native assets.
- Deny Lists: Block interactions with flagged addresses or contracts, mitigating risks from known vulnerabilities.